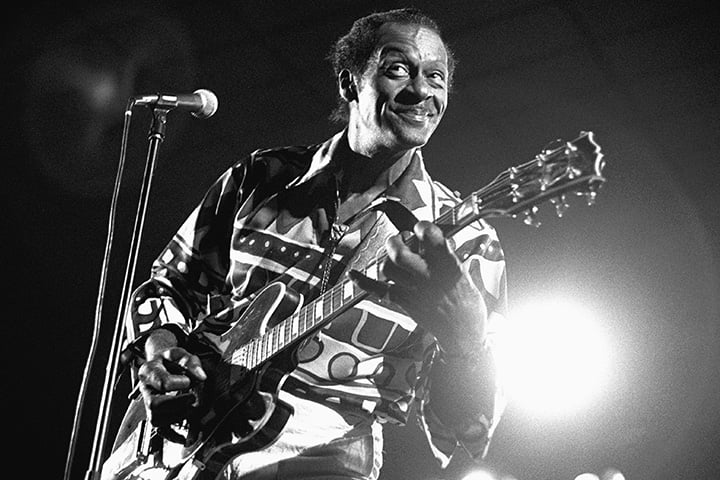
Chuck Berry, whose rollicking songs, springy guitar riffs and onstage duck walk defined rock & roll during its early years and for decades to come, died on Saturday. The St. Charles County Police Department confirmed the news on Facebook. Berry was 90 years old.
“St. Charles County police responded to a medical emergency on Buckner Road at approximately 12:40 p.m. today (Saturday, March 18),” the Facebook post reads. “Inside the home, first responders observed an unresponsive man and immediately administered lifesaving techniques. Unfortunately, the 90-year-old man could not be revived and was pronounced deceased at 1:26 p.m.” It went on to confirm that the man was Berry and added that his family was requesting privacy at this time.
While the exact cause of death is currently unknown, Berry’s son, Charles Jr., recently told Rolling Stone that he had suffered a bout of pneumonia. “Now what I can say is he’s a 90-year-old man,” he said. “And like most 90-year-old men, he has good days and he has bad days. In the not too distant past, he had a bout with pneumonia. He’s recovering, but it’s a much slower process for him to recover.”
Starting with his first hit, 1955’s “Maybellene,” Berry penned a collection of songs that, in both groove and teen-life mindset, became essential parts of the rock canon: “Roll Over, Beethoven,” “Rock & Roll Music,” and especially “Johnny B. Goode” were witty, zesty odes to the then-new art form – songs so key to the music that they had to be mastered by every fledgling guitarist or band who followed Berry. As teenagers, Keith Richards and Mick Jagger first bonded over their love of Berry’s music, and over the last five decades Berry’s songs have been covered by an astounding array of artists: from the Rolling Stones, the Beach Boys, the Kinks, the Doors and the Grateful Dead to James Taylor, Peter Tosh, Judas Priest, Dwight Yoakam, Phish, and Sex Pistols. As Richards said when inducting Berry into the Rock & Roll Hall of Fame in 1987, “I’ve stolen every lick he ever played.”
By fusing blues and country, Berry also invented a signature guitar style – like “ringing a bell,” as he put it in “Johnny G. Goode” – that was imitated by bands from the Stones and the Beach Boys to punk rockers. His lyrics – largely about sex, cars, music and trouble – introduced an entirely new vocabulary into popular music in the Fifties. In his songs, Berry captured America’s newfound post-war prosperity – a world, as he sang in “Back in the U.S.A.,” where “hamburgers sizzle on an open grill night and day.” ”I made records for people who would buy them,” Berry once said. “No color, no ethnic, no political – I don’t want that, never did.”
Yet Berry, in his role as rock & roll pioneer, also dealt with racism and bigotry, particularly when he was accused in 1961 of violating the Mann Act (transporting a woman or girl across state lines for purposes of prostitution). Berry claimed he had met Janice Norine Escalanti, a 14-year-old Native American, during a show in Texas and hired her to work at his St. Louis club, Club Bandstand. Imprisoned after a second trial (the first conviction was overturned due to the judge repeatedly using the word “nigra”), Berry, who pleaded not guilty, wound up serving nearly two years in prison and emerged a noticeably changed, bitter man. In recent years, he had mellowed somewhat, thanks in part to receiving a Lifetime Achievement Award at the Grammys in 1986 and being inducted into the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame.
Born in St. Louis on October 18th, 1926, Charles Edward Anderson Berry learned to play blues guitar as a teenager and first performed at his high school talent show. Music was his first love, but not necessarily his first career choice. The son of a carpenter, Berry worked on a General Motors assembly line and studied to be a hairdresser. With pianist Johnnie Johnson (a regular part of his band for years to come), Berry formed a band in 1952. After meeting blues legend Muddy Waters, Berry was introduced to Chess Records founder Leonard Chess in 1955. Berry brought along a song based on the country tune “Ida Red.” With a new title and lyrics – and an immediately grabby, grinding opening guitar lick — the song was transformed into “Maybellene.” On a return trip, Berry brought his recording of the song and was immediately signed to the label. “[Chess] couldn’t believe that a country tune (he called it a ‘hillbilly song’) could be written and sung by a black guy,” Berry later wrote in his 1987 memoir Chuck Berry: The Autobiography.
Love Music?
Get your daily dose of everything happening in Australian/New Zealand music and globally.
“Maybellene” hit Number Five in 1955 and established Berry’s career and sound. By the end of the 1950s, he had logged seven more top 40 hits: “Roll Over Beethoven” (Number 29), “School Day” (Number Three), “Rock & Roll Music” (Number Eight), “Sweet Little Sixteen” (Number Two), “Johnny B. Goode” (Number Eight), “Carol” (Number 28) and “Back in the U.S.A.” (Number 37). Although he was already in his early thirties by the time he scored those hits, Berry was unabashed about why he wrote for a younger audience. “Whatever would sell was what I thought I should concentrate on,” he wrote in his memoir, “so from ‘Maybellene’ on, I mainly improvised my lyrics toward the young adult and some even for the teeny boppers, as they called the tots then.”
Each song was defined by the Berry trademarks: that blend of propulsive beat, rueful charm, and ringing guitar. “The beautiful thing about Chuck Berry’s playing was it had such an effortless swing,” Keith Richards wrote in his memoir, Life. “None of this sweating and grinding away or grimacing, just pure, effortless swing like a lion.” During a 1956 concert, Berry was so self-conscious about only having brought one suit that he invented a new stage move “to hide the wrinkles,” as he told RS in 1969. That move, the duck walk, also became part of the rock & roll lexicon.
Intentionally or not, Berry also set the template for the rock & roll bad boy beyond his Mann Act conviction. Early in his life, Berry spent three years in reform school for an armed robbery attempt. In 1979, he was indicted for tax evasion and filing false income tax returns and spent three months in jail. (At his sentencing, he burst into tears.) In 1990, he was sued by several women who claimed Berry had videotaped them in the ladies’ room in his restaurant in St. Louis. (Berry reached an out-of-court settlement.)
When he was released from a Missouri prison in October 1963 after his Mann Act conviction, Berry was embittered, but he also saw his footprint all over a new generation of bands. The Beach Boys had released their first single, the Berry-influenced “Surfin’ Safari,” while a new band from England, the Rolling Stones, released Berry’s “Come On” as their first single in 1963. At first, Berry picked up where he left off, writing fine new songs like “You Never Can Tell” and “No Particular Place to Go” that held onto his devil-may-care attitude.
In 1966, Berry left Chess, his longtime home, for another label, Mercury, but the result was a series of sub-par albums and weak re-recordings of his hits. (One notable exception: a jam with the Steve Miller Band captured on the 1967 album, Live at the Fillmore Auditorium). In 1969, he returned to Chess – and returned to form – on harder-edged songs like “Tulane,” a drug-dealer romp that showed his newfound relevance. In 1972, he scored his first and only Number One pop hit with the novelty song, “My Ding-a-Ling.” His last album of original songs, Rock It, was released in 1979.
Berry was a notoriously tough and irascible character offstage. On tour, he long traveled alone, using backup bands hired by the promoters. He demanded payment in advance, a specific kind of amplifier and a limousine (with no driver) for his shows. In 1986, Richards assembled an all-star backup band (including Eric Clapton, Robert Cray, and sax player Bobby Keys) to play behind Berry in the documentary Hail! Hail! Rock ‘n’ Roll. Even then, Berry intimidated Richards onstage and off and only showed up on the first day of filming after he demanded an extra cash payment of $25,000. Despite those difficulties, the 1987 movie, directed by Taylor Hackford, became one of rock’s most acclaimed concert films.
In 2012, while visiting Cleveland to accept the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame’s American Music Masters Award, the then-86-year-old musician told Rolling Stone that he was slowing down with age. “I am hearing very little,” he said. “I’m wondering about my future. That’s news!
“Well, I’ll give you a little piece of poetry,” he added, when asked to expand. “Give you a song? I can’t do that. My singing days have passed. My voice is gone. My throat is worn. And my lungs are going fast. I think that explains it.”
Up until 2014, Berry continued to perform at clubs and casinos. Once a month, he played at Blueberry Hill, a restaurant and bar in St. Louis, where his October 2014 show marked his 209th consecutive show at the venue, according to Riverfront Times.
Berry lived in St. Louis but often spent time at Berry Park, a 155-acre property in nearby Wentzville, Missouri. (As he told Rolling Stone in 2010, he even still mowed the lawn there.) Asked by RS in 1969 about rock’s role, Berry said, “Like any music, it brings you together, because if two people like the same music, they can be standing beside each other shaking and they wind up dancing, and that’s a matter of communication … so I say it’s a means of communication, more so than other music, to the kids.”
He is survived by his wife Themetta “Toddy” Suggs, whom he married in 1948, and four children.